Introduction
Preventing false alarms: Imagine a bustling office building where the fire alarm goes off for the third time this month. Panic ensues, employees evacuate, and the local fire department rushes to the scene. Upon arrival, they discover yet another false alarm. This scenario is all too common; in fact, false alarms account for up to 30% of all fire department calls in some urban areas, according to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA).
Importance of Topic: Preventing false alarms in fire alarm systems is not just a matter of convenience; it’s crucial for safety, efficiency, and resource management. False alarms can desensitize people to the sound of the alarm, leading to slower reactions during an actual emergency. They also divert emergency responders away from real emergencies, potentially putting lives at risk. Additionally, frequent false alarms can lead to financial penalties and wasted resources for businesses and municipalities.
Purpose of the Post: In this blog post, we’ll delve into practical tips and strategies to prevent false alarms in fire alarm systems. You’ll learn about the common causes of false alarms, how to properly install and maintain fire alarm systems, the role of environmental factors, and the benefits of advanced detection technologies. By implementing these strategies, you can reduce the frequency of false alarms, ensuring that your fire alarm system remains reliable and effective in protecting lives and property.
Understanding False Alarms
Definition of False Alarms:
A false alarm in fire alarm systems occurs when the alarm is triggered without the presence of a genuine fire threat. These incidents can stem from a variety of non-emergency stimuli that cause the system to activate, resulting in unnecessary evacuations and emergency responses.
Common Causes:
False alarms can arise from numerous sources. Here are some of the most common:
- Cooking Smoke: Cooking activities can easily produce smoke or steam that triggers smoke detectors, especially in areas near kitchens without proper ventilation.
- Dust and Dirt: Dust particles can accumulate in and around smoke detectors, leading to false activations. Construction or renovation activities can exacerbate this issue by creating excessive airborne particles.
- Steam: Bathrooms and other areas with high humidity can produce steam that mimics the presence of smoke, causing the alarm to go off.
- Aerosol Sprays: Products like hair sprays, cleaning agents, and aerosol-based products can set off smoke detectors.
- Technical Malfunctions: Faulty or poorly maintained equipment can lead to false alarms. This includes issues such as low batteries, electrical faults, or software glitches.
- Environmental Factors: Sudden temperature changes, insects, and other environmental conditions can also trigger false alarms.
Statistics and Impact:
False alarms are a significant issue across various sectors. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), false alarms represent roughly 10% to 30% of all fire-related calls in many urban settings. In the United States alone, fire departments respond to millions of false alarms annually.
The impact of these false alarms is far-reaching:
- Desensitization: Frequent false alarms can lead to complacency among building occupants, causing delayed responses during actual emergencies.
- Resource Strain: Each false alarm diverts emergency services away from real emergencies, wasting valuable time and resources. This can be particularly critical in densely populated areas where fire departments are already stretched thin.
- Financial Costs: Businesses and building owners can face significant financial repercussions, including fines from local authorities, increased insurance premiums, and operational disruptions.
- Operational Disruptions: Repeated evacuations disrupt business operations, leading to loss of productivity and potential financial losses.
By understanding what constitutes a false alarm and the common causes, we can take informed steps to mitigate their occurrence, ensuring that fire alarm systems function optimally and emergency responses are reserved for genuine threats.
Types of Fire Alarm Systems
Conventional Fire Alarms
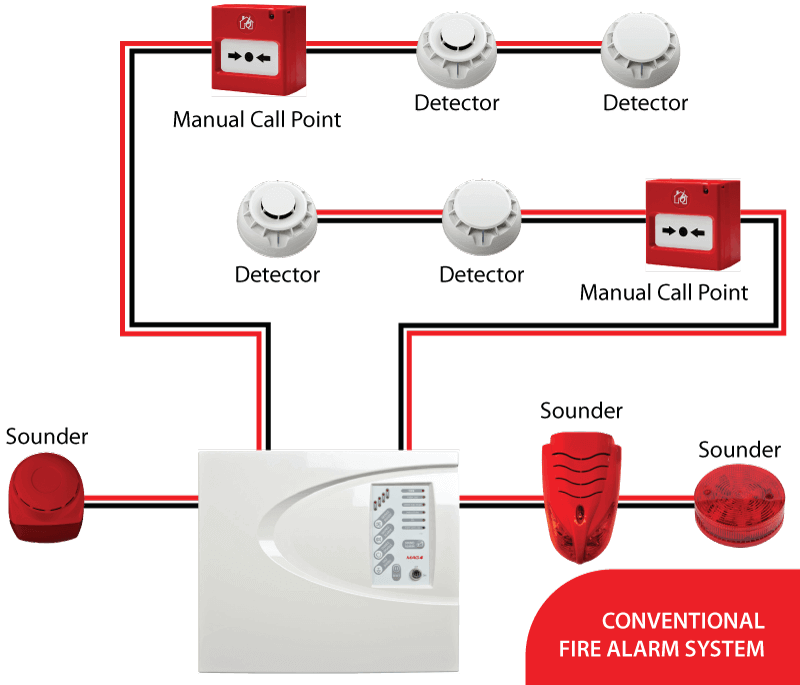
How They Work:
Conventional fire alarm systems are the most basic type of fire alarm system. They divide the protected premises into zones, each connected to a central control panel. When a detector or manual call point in one of these zones is activated, it triggers the alarm for that specific zone. This alerts building occupants and emergency responders to the general area where the fire might be located.
Susceptibility to False Alarms:
These systems are more prone to false alarms because they lack the ability to precisely identify the source of the alarm. Any sensor within a zone triggering the alarm can cause the entire zone to be considered as the source of the fire, leading to potential overreaction to non-emergency stimuli such as dust, steam, or minor electrical faults.
Addressable Fire Alarms
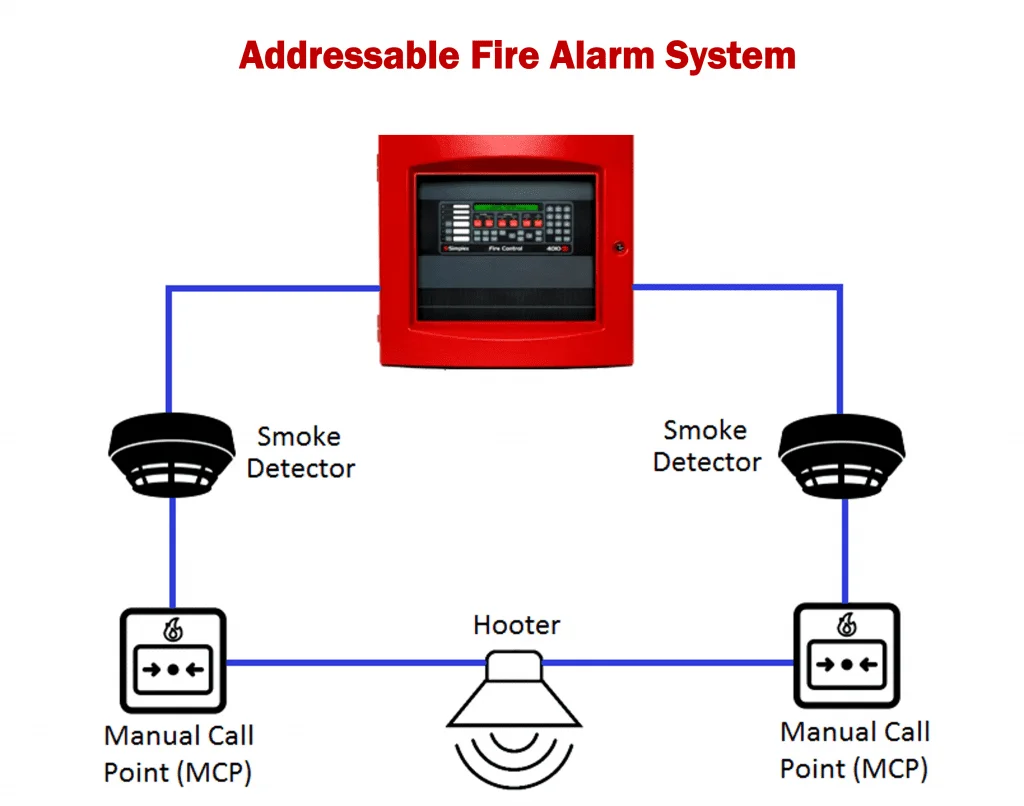
Functionality:
Addressable fire alarm systems offer a more sophisticated approach by giving each device on the system a unique address. This allows the control panel to communicate with individual detectors and call points, pinpointing the exact location of an activated device. This precise identification helps in quicker and more targeted responses to potential fires.
Advantages in Reducing False Alarms:
Addressable systems can significantly reduce false alarms by providing detailed information about each activation. For instance, maintenance teams can identify and address specific devices that frequently cause false alarms. Additionally, advanced diagnostics can distinguish between different types of particles (such as dust or smoke) and adjust sensitivity accordingly, minimizing the likelihood of false triggers.
Smart Fire Alarm Systems

Modern Advancements:
Smart fire alarm systems represent the latest in fire detection technology, incorporating elements of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). These systems use advanced algorithms and data analytics to improve detection accuracy and reliability.
How Smart Technology preventing false alarms:
- Multi-Sensor Detection: Smart alarms often use multiple types of sensors (e.g., smoke, heat, carbon monoxide) in a single device. This allows the system to cross-reference data from different sensors to confirm the presence of a fire, reducing the likelihood of false alarms from non-fire-related stimuli.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI can analyze patterns and learn from past incidents to better distinguish between real fires and false alarms. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to recognize and ignore common false alarm triggers such as cooking smoke or steam.
- Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics: Smart systems can be monitored and managed remotely. This capability allows for real-time diagnostics and maintenance, ensuring that any potential issues causing false alarms are addressed promptly.
- Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS): Integration with BMS enables fire alarm systems to work in conjunction with other building systems (such as HVAC or security systems) to create a holistic approach to building safety. For example, if a fire alarm is triggered, the BMS can automatically adjust ventilation systems to minimize smoke spread.
By leveraging these advanced technologies, smart fire alarm systems provide a more reliable and efficient means of detecting fires while significantly reducing the occurrence of false alarms. This not only enhances safety but also ensures that emergency services are utilized effectively.
Proper Installation and Maintenance To Preventing false alarms
Professional Installation
Importance of Professional Installation:
Ensuring that fire alarm systems are installed by qualified professionals is critical for their effectiveness and reliability. Professional installers have the necessary expertise to correctly place detectors and alarms, ensuring optimal coverage and sensitivity. They understand the intricacies of different fire alarm systems and adhere to local building codes and safety regulations. This not only minimizes the risk of false alarms but also ensures that the system functions correctly in the event of an actual fire.
Regular Maintenance To Preventing False Alarms
Maintenance Checklist:
Regular maintenance is essential to keep fire alarm systems in good working order. Here’s a detailed checklist for maintaining fire alarm systems:
- Cleaning Detectors: Dust, dirt, and other debris can accumulate on detectors, reducing their sensitivity and increasing the likelihood of false alarms. Clean detectors regularly using a vacuum or soft brush.
- Testing Alarms: Conduct monthly tests of the alarm system to ensure that all components are functioning correctly. This includes sounding the alarms and checking that the control panel receives signals from all detectors and manual call points.
- Checking Batteries: Ensure that all batteries in the system, especially in backup power supplies, are in good condition. Replace any weak or expired batteries to maintain uninterrupted operation.
- Inspecting Wiring and Connections: Check all wiring and electrical connections for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Faulty wiring can lead to malfunctions and false alarms.
- Verifying Sensor Calibration: Ensure that all sensors are calibrated correctly. Incorrect calibration can lead to either a failure to detect fires or an increase in false alarms.
- Updating Logs: Maintain detailed logs of all maintenance activities, including dates, actions taken, and any issues identified. This helps in tracking the system’s health over time and planning future maintenance activities.
System Updates
Importance of Keeping Firmware and Software Up to Date:
Just like any other technological system, fire alarm systems benefit from regular updates to their firmware and software. Manufacturers frequently release updates to improve system performance, enhance security, and address any identified bugs or vulnerabilities. Keeping the system’s software up to date ensures that it operates with the latest enhancements and protections.
- Improved Functionality: Updates can provide new features or improve existing ones, enhancing the system’s overall performance and reliability.
- Enhanced Security: Regular updates help protect the system from cybersecurity threats, ensuring that unauthorized access is prevented.
- Bug Fixes: Software updates often include fixes for known issues, reducing the likelihood of malfunctions and false alarms.
Regularly check with the manufacturer or service provider for available updates and ensure that they are installed promptly. This proactive approach ensures that the fire alarm system remains reliable and efficient, providing the best possible protection for the building and its occupants.
By emphasizing professional installation, adhering to a rigorous maintenance schedule, and keeping systems updated, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of false alarms while ensuring that the fire alarm system is ready to perform in an actual emergency.
Environmental Considerations
Placement of Detectors
Best Practices for Detector Placement:
Proper placement of fire detectors is crucial to minimize false alarms. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Avoid Kitchens and Bathrooms: Kitchens and bathrooms are common sources of false alarms due to cooking smoke, steam, and aerosol sprays. Instead, place detectors near these areas but not directly within them. Use heat detectors in kitchens as they are less likely to be triggered by cooking activities.
- High-Ceilinged Areas: Install detectors at appropriate heights in rooms with high ceilings to ensure smoke or heat reaches the detector. Avoid placing detectors near air vents, fans, or windows where airflow might disperse smoke before it reaches the detector.
- Mechanical Rooms and Garages: These areas often contain equipment that can produce dust, fumes, or heat. Use specialized detectors designed for these environments to reduce false alarms.
- Hallways and Common Areas: Place detectors in hallways and common areas to ensure wide coverage while avoiding spaces prone to false triggers.
Environmental Controls
Managing Humidity, Ventilation, and Dust Levels:
Effective environmental controls can significantly reduce the risk of false alarms:
- Humidity Control: High humidity can cause condensation inside detectors, leading to false alarms. Use dehumidifiers in areas prone to high humidity, such as basements and bathrooms, to maintain optimal humidity levels.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation to prevent steam and smoke from lingering in areas like kitchens and bathrooms. Use exhaust fans and open windows to disperse smoke and steam quickly.
- Dust Management: Regular cleaning and maintenance can prevent dust from accumulating on detectors. In environments with high dust levels, such as construction sites or workshops, consider using dust covers for detectors or opting for detectors with built-in dust compensation features.
Specialized Detectors
Using Heat Detectors or Dual-Sensor Alarms:
- Heat Detectors: Heat detectors are less sensitive to smoke and steam, making them ideal for kitchens, garages, and other areas where traditional smoke detectors might trigger false alarms. They activate when a certain temperature threshold is reached or when there is a rapid increase in temperature.
- Dual-Sensor Alarms: Dual-sensor alarms combine both smoke and heat detection technologies, providing a more reliable detection method. They can distinguish between different types of fire signatures, reducing the likelihood of false alarms. These detectors are particularly useful in areas with variable environmental conditions.
- Photoelectric and Ionization Sensors: In some cases, using photoelectric sensors (which are better at detecting slow, smoldering fires) or ionization sensors (which are more responsive to fast, flaming fires) can be advantageous. Choosing the right type of sensor for each location can help reduce false alarms.
By carefully considering the placement of detectors, managing environmental factors, and utilizing specialized detectors where necessary, you can significantly minimize the occurrence of false alarms. This ensures that the fire alarm system remains reliable and responsive, providing accurate alerts when they are truly needed.
Training and Education
Training Occupants
Importance of Educating Building Occupants:
Educating building occupants on the causes of false alarms and how to prevent them is a crucial step in minimizing unnecessary activations. When occupants understand the common triggers of false alarms and how their actions can impact the system, they are more likely to take preventive measures. Here’s how to effectively educate building occupants:
- Awareness Programs: Conduct regular awareness sessions to inform occupants about the sensitivity of fire alarm systems. Highlight activities that can trigger false alarms, such as cooking without proper ventilation, using aerosol sprays near detectors, or causing dust disturbances during cleaning or renovations.
- Instructional Materials: Distribute easy-to-understand instructional materials, such as brochures, emails, or posters, outlining do’s and don’ts to avoid false alarms.
- Interactive Training: Utilize interactive training methods such as videos, demonstrations, or workshops to engage occupants and reinforce the importance of preventing false alarms.
Regular Drills
Conducting Fire Drills:
Regular fire drills are essential for ensuring that everyone knows the correct procedures during an alarm without causing unnecessary activations. Here’s how to conduct effective fire drills:
- Scheduled Drills: Plan and schedule regular fire drills, ensuring they occur at different times to test the preparedness of all building occupants.
- Clear Protocols: Establish clear protocols for fire drills, including designated evacuation routes, assembly points, and roles for staff or fire wardens.
- Simulate Different Scenarios: Include various scenarios in the drills, such as blocked exits or alarms triggered from different parts of the building, to ensure comprehensive preparedness.
- Feedback and Improvement: After each drill, gather feedback from participants to identify any issues or areas for improvement. Use this feedback to refine procedures and enhance overall readiness.
Signage and Instructions
Clear Signage to Guide Actions:
Providing clear signage and instructions throughout the building can help occupants respond appropriately during both false alarms and real emergencies. Effective signage and instructions include:
- Evacuation Routes: Clearly mark all evacuation routes and exits with visible signs. Ensure these signs are illuminated and visible even in low-light conditions.
- Assembly Points: Designate and mark assembly points where occupants should gather after evacuating. Include signs directing people to these locations.
- Alarm Response Instructions: Place signs near alarm pull stations and detectors with instructions on what to do if the alarm sounds. This can include reminders not to tamper with detectors and to report any accidental activations immediately.
- Educational Posters: Display posters in common areas, such as lobbies and break rooms, with tips on preventing false alarms and actions to take during an alarm.
- Digital Signage: Use digital signage where possible to provide real-time updates and instructions during an emergency or false alarm.
By prioritizing training and education, conducting regular fire drills, and providing clear signage and instructions, building occupants will be better equipped to prevent false alarms and respond appropriately during real emergencies. This proactive approach not only reduces the frequency of false alarms but also enhances the overall safety and preparedness of the building’s occupants.
Technological Solutions ,Preventing false alarms
Advanced Detection Technologies
Introduction to Multi-Sensor and AI-Based Detection Systems:
Modern advancements in fire detection technology have significantly improved the accuracy and reliability of fire alarm systems. Two key innovations are multi-sensor detectors and AI-based detection systems.
- Multi-Sensor Detectors: Multi-sensor detectors combine various types of sensors, such as smoke, heat, and carbon monoxide, within a single device. By analyzing data from multiple sources, these detectors can more accurately determine whether there is a real fire threat. For instance, a multi-sensor detector can differentiate between smoke from a small kitchen incident and smoke from a genuine fire, reducing false alarms.
- AI-Based Detection Systems: Artificial intelligence (AI) is being increasingly integrated into fire alarm systems to enhance detection accuracy. AI algorithms can analyze patterns and learn from past data to distinguish between real fires and false triggers. For example, AI can differentiate between steam from a shower and smoke from a fire by recognizing unique characteristics. These systems continuously improve over time, becoming more adept at preventing false alarms.
Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS)
How Integrating Fire Alarms with BMS Can Help in Accurate Detection and Response:
Integrating fire alarm systems with Building Management Systems (BMS) provides a holistic approach to building safety and efficiency.
- Centralized Control: A BMS integrates various building systems, including HVAC, lighting, security, and fire alarms, into a centralized control platform. This integration allows for coordinated responses during an emergency. For example, if a fire alarm is triggered, the BMS can automatically shut down ventilation systems to prevent the spread of smoke and activate emergency lighting to guide occupants to exits.
- Enhanced Data Analysis: By combining data from multiple building systems, a BMS can provide more accurate information about the situation. For example, data from security cameras and access control systems can help verify the presence of a fire, reducing the chances of false alarms.
- Automated Responses: Integration with BMS allows for automated responses that can enhance safety. For instance, if the fire alarm system detects smoke, the BMS can automatically unlock exit doors, activate fire suppression systems, and alert building management.
Remote Monitoring
Benefits of Remote Monitoring Services:
Remote monitoring services offer several advantages in enhancing the reliability and effectiveness of fire alarm systems.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Remote monitoring services provide 24/7 surveillance of fire alarm systems. Trained operators can assess alarms in real-time, ensuring prompt and appropriate responses. This constant vigilance helps in quickly identifying and addressing any issues that may arise.
- Verification of Alarms: One of the significant benefits of remote monitoring is the ability to verify alarms before dispatching emergency services. When an alarm is triggered, remote operators can use additional data from integrated systems (such as security cameras) to confirm whether it is a false alarm or a real fire. This verification process reduces the number of unnecessary emergency dispatches, saving resources and preventing desensitization among building occupants.
- Immediate Alerts and Notifications: Remote monitoring services can provide instant alerts and notifications to building managers, occupants, and emergency responders. These alerts can be customized to notify specific individuals or groups, ensuring that the right people are informed promptly.
- Proactive Maintenance: Remote monitoring can also include predictive maintenance services. By continuously analyzing the performance of the fire alarm system, remote monitoring services can identify potential issues before they become serious problems. This proactive approach ensures that the system remains in optimal working condition, further reducing the likelihood of false alarms.
By leveraging advanced detection technologies, integrating fire alarms with Building Management Systems, and utilizing remote monitoring services, you can significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability of fire alarm systems. These technological solutions not only help in preventing false alarms but also ensure a swift and effective response in the event of a real fire, thereby improving overall safety and efficiency.
Policy and Regulation Compliance
Adhering to Codes
Overview of Fire Alarm Regulations and Standards:
Fire alarm systems must adhere to various regulations and standards designed to ensure their effectiveness and reliability. Compliance with these codes helps reduce the incidence of false alarms and enhances overall safety.
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA): The NFPA provides a comprehensive set of codes and standards for fire safety, including the NFPA 72 National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code. This code outlines the installation, maintenance, and testing requirements for fire alarm systems, helping to minimize false alarms.
- International Fire Code (IFC): The IFC, developed by the International Code Council (ICC), includes regulations for fire alarm system design, installation, and maintenance. Adhering to the IFC ensures that systems are correctly implemented and maintained, reducing the likelihood of false alarms.
- Local Fire Codes: In addition to national and international standards, local jurisdictions often have their own fire codes and regulations. These can include specific requirements for detector placement, system testing, and maintenance practices tailored to the local environment.
Building Codes and Fire Safety Standards
Ensuring Compliance with Local Building Codes and Fire Safety Standards:
Compliance with local building codes and fire safety standards is crucial for the effectiveness of fire alarm systems. These codes are designed to ensure that buildings are equipped with appropriate fire detection and suppression systems that function correctly.
- Design and Installation: Building codes specify the design and installation requirements for fire alarm systems, including the type and placement of detectors, wiring standards, and integration with other safety systems. Following these guidelines ensures that systems are installed correctly, reducing the chances of false alarms.
- Occupancy-Specific Standards: Different types of buildings (e.g., residential, commercial, industrial) have specific fire safety standards tailored to their unique risks. Ensuring compliance with these standards helps address the particular challenges of each occupancy type, enhancing overall safety.
- Regular Updates: Building codes and fire safety standards are regularly updated to incorporate new technologies and best practices. Staying informed about these updates and implementing necessary changes ensures ongoing compliance and system effectiveness.
Regular Audits and Inspections To preventing false alarms
Importance of Conducting Regular Audits and Inspections:
Regular audits and inspections are vital to maintaining the reliability and effectiveness of fire alarm systems. They help identify potential issues before they lead to false alarms or system failures.
- Routine Inspections: Regular inspections, conducted by qualified professionals, ensure that all components of the fire alarm system are functioning correctly. This includes checking detectors, control panels, wiring, and power supplies.
- Functional Testing: Periodic testing of the entire fire alarm system verifies that alarms, detectors, and communication devices operate as intended. Functional testing helps identify any faults or malfunctions that could cause false alarms.
- Compliance Audits: Comprehensive audits assess the system’s compliance with relevant codes and standards. These audits review installation practices, maintenance records, and system performance to ensure ongoing adherence to regulations.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintaining detailed records of all inspections, tests, and maintenance activities is essential. These records provide a history of the system’s performance and compliance, helping to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Proactive Maintenance: Audits and inspections support proactive maintenance by identifying issues early. Addressing these issues promptly prevents them from escalating into more significant problems, reducing the risk of false alarms.
By adhering to fire alarm regulations and standards, ensuring compliance with local building codes and fire safety standards, and conducting regular audits and inspections, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of false alarms. This approach not only enhances system reliability but also ensures that fire alarm systems provide accurate and timely alerts in the event of a real fire, thereby protecting lives and property.
Conclusion (preventing false alarms)
Preventing false alarms in fire alarm systems is essential for safety, efficiency, and resource management. We encourage you to implement the strategies discussed in this post to minimize false alarms and ensure your fire alarm system operates effectively. Stay proactive about maintenance, educate building occupants, leverage advanced technologies, and adhere to all relevant regulations and standards. By taking these steps, you can enhance the reliability of your fire alarm system, protect lives, and ensure a safer environment for everyone.


